How to install Wazuh server on Rocky Linux? In this tutorial, you will learn how to install Wazuh server on Rocky Linux. Wazuh is a free, open source and enterprise-ready security monitoring solution that helps you to gain security visibility into your infrastructure by monitoring hosts at an operating system and application level. It provides the following capabilities:
- log analysis
- file integrity monitoring
- intrusions detection
- policy and compliance monitoring
Install Wazuh Server on Rocky Linux
There are different deployment architectures for Wazuh server:
All-in-one deployment– Wazuh and the ELK stack components are installed on a single server.Multi-node (Distributed) deployment– Wazuh and ELK stack components are installed on separate nodes.
In this setup, we will install both Wazuh server and ELK stack components on the same node.
You can check the requirements page before you can proceed.
Install Wazuh Server on Rocky Linux
In order to install and setup Wazuh server on Rocky Linux, there are two components that needs to be installed.
Install Wazuh Manager on Rocky Linux
Create Wazuh Repository
Rocky Linux do not have Wazuh manager package on its repository list. As such you need to install Wazuh repository as follows;
Install Wazuh repository GPG key;
rpm --import https://packages.wazuh.com/key/GPG-KEY-WAZUHInstall the Wazuh 4.x repository (current stable release as of this writing is v4.3.10);
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/wazuh.repo << EOF [wazuh] gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://packages.wazuh.com/key/GPG-KEY-WAZUH enabled=1 name=EL-\$releasever - Wazuh baseurl=https://packages.wazuh.com/4.x/yum/ protect=1 EOF
Confirm the available version of Wazuh manager;
dnf info wazuh-manager
Name : wazuh-manager Version : 4.3.10 Release : 1 Architecture : x86_64 Size : 115 M Source : wazuh-manager-4.3.10-1.src.rpm Repository : wazuh
As you can see, Wazuh manager 4.3.10 is the current release as provided by the repos.
Therefore, Install Wazuh Manager on Rocky Linux by running the command below;
dnf install wazuh-manager
Running Wazuh manager
Once the installation is done, run the command below to start and enable it to run on system boot;
systemctl enable --now wazuh-manager
Checking the status;
systemctl status wazuh-manager
Install ELK Stack on Rocky Linux
Since we are using a single node deployment architecture, we will install ELK stack as well on the same node.
Wazuh app requires Kibana to allow you access Wazuh manager dashboard. Elasticsearch is required as it provides a distributed, multitenant-capable full-text search engine.
You will also need Filebeat, that collect Wazuh manager event data and pushes them to Elasticsearch.
As of this writing, Wazuh 4.3.10 supports ELK 7.17.6 as per the compatibility matrix.
Therefore, the installation commands below installs ELK stack 7.17.6 on Rocky Linux.
Install the ELK/Elastic YUM repository
Install the ELK/Elastic repository to enable you install the stack components. Begin by importing the ELK stack repository PGP signing Key;
rpm --import https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
If the above fails with the error;
error: https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch: key 1 import failed.Run the following;
update-crypto-policies --set DEFAULT:SHA1Re-import the key;
rpm --import https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearchInstall ELK APT repository on Rocky Linux.
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/wazuh.repo << 'EOF' [elasticsearch] name=Elasticsearch repository for 7.x packages baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/yum gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=0 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md EOF
Installing Elasticsearch
Note, since the installation is done from the ELK YUM repositories, you will get the current latest and stable versions installed. However, we need version 7.17.6. Hence, use the command below to install ES v7.17.6.
dnf install --enablerepo=elasticsearch elasticsearch-7.17.6
You can list available versions of a package using the command;
dnf info --enablerepo=elasticsearch elasticsearch
Sample installation output;
Dependencies resolved. ============================================================================================================================================================================ Package Architecture Version Repository Size ============================================================================================================================================================================ Installing: elasticsearch x86_64 7.17.6-1 elasticsearch 294 M Transaction Summary ============================================================================================================================================================================ Install 1 Package Total download size: 294 M Installed size: 488 M Is this ok [y/N]: y Downloading Packages: elasticsearch-7.17.6-x86_64.rpm 2.1 MB/s | 294 MB 02:19 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 2.1 MB/s | 294 MB 02:19 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Running scriptlet: elasticsearch-7.17.6-1.x86_64 1/1 Creating elasticsearch group... OK Creating elasticsearch user... OK Installing : elasticsearch-7.17.6-1.x86_64 1/1 Running scriptlet: elasticsearch-7.17.6-1.x86_64 1/1 ### NOT starting on installation, please execute the following statements to configure elasticsearch service to start automatically using systemd sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch.service ### You can start elasticsearch service by executing sudo systemctl start elasticsearch.service Created elasticsearch keystore in /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.keystore /usr/lib/tmpfiles.d/elasticsearch.conf:1: Line references path below legacy directory /var/run/, updating /var/run/elasticsearch → /run/elasticsearch; please update the tmpfiles.d/ drop-in file accordingly. Verifying : elasticsearch-7.17.6-1.x86_64 1/1 Installed: elasticsearch-7.17.6-1.x86_64 Complete!
Configuring Elasticsearch
Once the installation is done, proceed to configure Elasticsearch. The default configuration file for Elasticsearch is /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml.
Open the configuration file for editing using your preferred text editor;
vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
You can optionally set the name of the cluster or go with the default;
# ---------------------------------- Cluster -----------------------------------
...
cluster.name: wazuh-elkFor the network settings, we will the defaults since by default, it uses the loopback interface and port 9200/tcp, which is fine for our case as we will only be accessing Elasticsearch locally from the Wazuh server.
By default, Elasticsearch tries to discovers other nodes to form a cluster when started. Since we are running a single node cluster, you need to specify the same by inserting the line, discovery.type: single-node, under the Discovery section.
# --------------------------------- Discovery ----------------------------------
...
discovery.type: single-nodeSave and exit the file.
Configure the JVM heap size and set it to about half the memory available on the system.
vim /etc/elasticsearch/jvm.options.d/jvm.options
-Xms512m
-Xmx512mSave and exit the file.
There are other important Elasticsearch configuration settings you should consider, especially if you are taking it to production. Check the Import Elasticsearch Configuration page for more tips.
Running Elasticsearch
Once you are done with Elasticsearch configurations, start and enable Elasticsearch to run on system boot.
systemctl enable --now elasticsearch
Checking the status;
systemctl status elasticsearch
You can use curl to verify if all is well with Elasticsearch;
curl http://localhost:9200
{
"name" : "rocky9",
"cluster_name" : "wazuh-elk",
"cluster_uuid" : "hpGPgKhYRpetfkWh2oIjzw",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.17.6",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "rpm",
"build_hash" : "f65e9d338dc1d07b642e14a27f338990148ee5b6",
"build_date" : "2022-08-23T11:08:48.893373482Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.11.1",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Install and Configure Kibana
Install Kibana 7.17.6 by running the command;
dnf install --enablerepo=elasticsearch kibana-7.17.6
Once the installation is done, you can configure Kibana. The default configuration file for Kibana is /etc/kibana/kibana.yml. Open the file editing.
vim /etc/kibana/kibana.ymlThe default host and port settings configure Kibana to run on localhost:5601. We need to change, the host especially, to enable us to reach Kibana externally.
# Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use.
# server.port: 5601
server.port: 5601
...
# To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address.
#server.host: "localhost"
server.host: "192.168.56.144"Next, you need to configure how Kibana will connect to Elasticsearch. By default, as depicted by the setting below, Kibana can connect to Elasticsearch on loopback address, that is only if Elasticsearch is set to listen on the loopback interface.
# The URLs of the Elasticsearch instances to use for all your queries.
#elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]Be sure to set the IP address if ES is set to listen on a non-loopback IP address.
In its basic setup, that is just enough for Kibana.
Save and exit the file.
Running Kibana
Now start and enable Kibana to run on system boot;
systemctl enable --now kibana
Check the status;
systemctl status kibana
Install Filebeat
You need to install same version of Filebeat as Elasticsearch and Kibana.
dnf install --enablerepo=elasticsearch filebeat-7.17.6
Filebeat will be used to ship event data from Wazuh to Elasticsearch.
Configuring Filebeat
Setup Filebeat configuration.
mv /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml{,.bak}
cat > /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml << EOL
# Wazuh - Filebeat configuration file
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["127.0.0.1:9200"]
setup.template.json.enabled: true
setup.template.json.path: '/etc/filebeat/wazuh-template.json'
setup.template.json.name: 'wazuh'
setup.ilm.overwrite: true
setup.ilm.enabled: auto
filebeat.modules:
- module: wazuh
alerts:
enabled: true
archives:
enabled: false
seccomp:
default_action: allow
syscalls:
- action: allow
names:
- rseq
logging.level: info
logging.to_files: true
logging.files:
path: /var/log/filebeat
name: filebeat
keepfiles: 7
permissions: 0644
EOL
Save and exit the configuration file.
Install Filebeat Wazuh Module
Download and install Filebeat Wazuh module;
wget https://packages.wazuh.com/4.x/filebeat/wazuh-filebeat-0.2.tar.gz -P /tmp/
mkdir /usr/share/filebeat/module/wazuh
tar xzf /tmp/wazuh-filebeat-0.2.tar.gz -C /usr/share/filebeat/module/wazuh/ --strip-components=1
Load Wazuh Elasticsearch Index Template to Elasticsearch
Download and load the Wazuh Elasticsearch alerts index template.
curl -so /etc/filebeat/wazuh-template.json \ https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wazuh/wazuh/4.3/extensions/elasticsearch/7.x/wazuh-template.json
chmod go+r /etc/filebeat/wazuh-template.json
Next, load the template;
filebeat setup \ --path.config /etc/filebeat \ --path.home /usr/share/filebeat \ --path.data /var/lib/filebeat \ --index-management -E setup.template.json.enabled=false
Test Filebeat connection to Elasticsearch
filebeat test output
elasticsearch: http://127.0.0.1:9200...
parse url... OK
connection...
parse host... OK
dns lookup... OK
addresses: 127.0.0.1
dial up... OK
TLS... WARN secure connection disabled
talk to server... OK
version: 7.17.6
Start and enable Filebeat to run on system boot;
systemctl daemon-reload systemctl enable --now filebeat
Check status;
systemctl status filebeatFor logs;
tail -f /var/log/filebeat/filebeatInstall Wazuh App Kibana Plugin
You can now install Wazuh app Kibana plugin. Before you can proceed, ensure that you set the owner of the directories, /usr/share/kibana/optimize/ and /usr/share/kibana/plugins to kibana.
[ ! -d "/usr/share/kibana/{optimize,plugins,data}" ] && mkdir /usr/share/kibana/{optimize,plugins,data}chown -R kibana: /usr/share/kibana/{optimize,plugins,data}Navigate to Kibana home directory;
cd /usr/share/kibana
The install Wazuh App for Kibana 7.17.6;
sudo -u kibana /usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana-plugin \ install https://packages.wazuh.com/4.x/ui/kibana/wazuh_kibana-4.3.10_7.17.6-1.zip
install https://packages.wazuh.com/4.x/ui/kibana/wazuh_kibana-4.3.10_7.17.6-1.zip Attempting to transfer from https://packages.wazuh.com/4.x/ui/kibana/wazuh_kibana-4.3.10_7.17.6-1.zip Transferring 30325453 bytes.................... Transfer complete Retrieving metadata from plugin archive Extracting plugin archive Extraction complete Plugin installation complete
You can list installed plugins;
sudo -u kibana /usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana-plugin list
[email protected]Start Kibana;
systemctl enable --now kibana
Restart Elasticsearch and Wazuh-manager;
systemctl restart elasticsearch wazuh-manager
Once they are up, if you check the created indices, you should be able to see wazuh-alerts* index created;
curl -s localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v | grep wazuh
Accessing the Wazuh App on Kibana
Accessing Kibana Interface
Now that your ELK stack is running, you can access Kibana interface, http://<server-IP-or-resolvable-hostname>:5601.
Ensure that you open Port 5601/TCP on firewall, to allow external access to Kibana.
firewall-cmd --add-port=5601/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --reload
When you land on Kibana Interface, navigate to the menu and scroll down to see the Wazuh App. See example screenshot below;
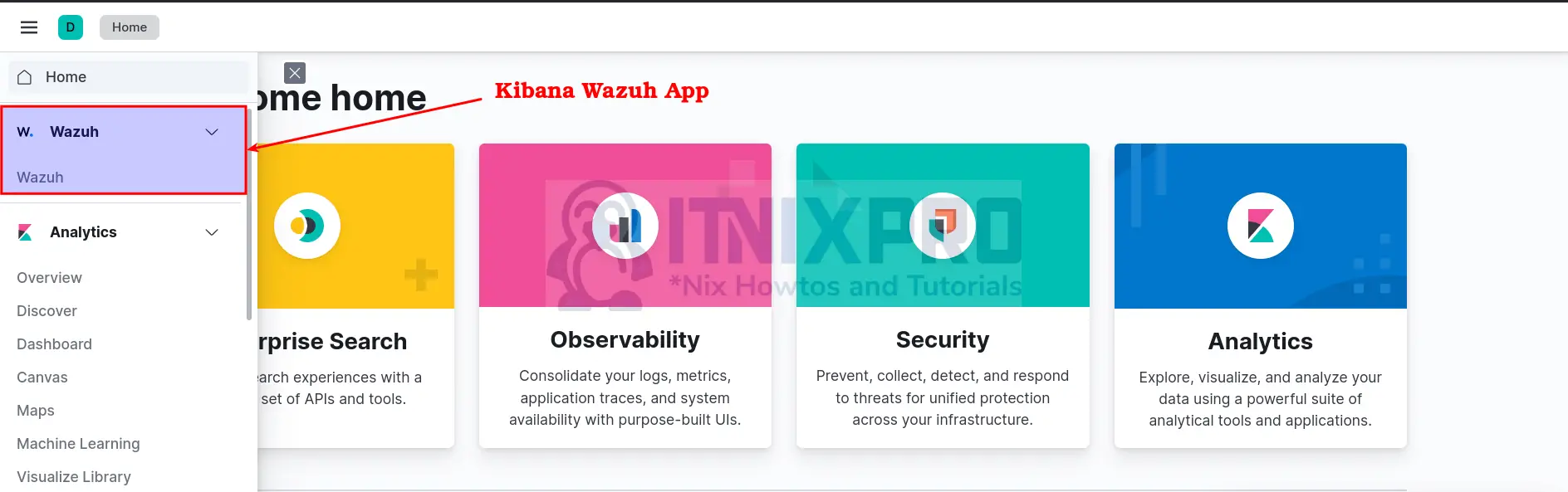
Upon clicking the app, it checks a few things like the Wazuh API connection and the version, the availability of the default indices such as wazuh-alerts-* (default index).
If all is well, you should land on the Wazuh dashboard;
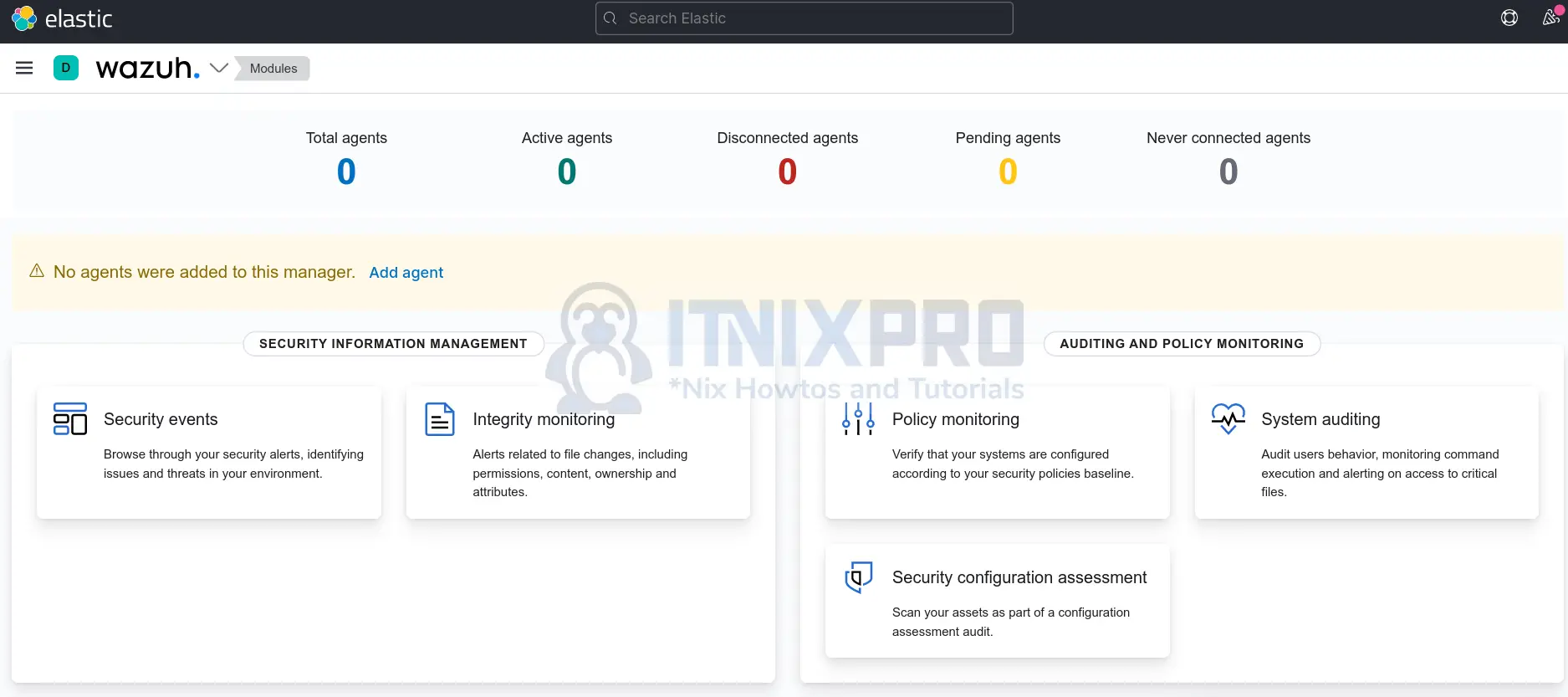
And that marks the end of our guide on how to install Wazuh server with ELK stack on Rocky Linux.
In our next guides, we will learn on how to install to and add Wazuh agents on end points being monitored to collect and ship data to Kibana for visualization.
Other Tutorials
Configure Elastic Endpoint Security Malware Detection and Prevention
