This guide will go through how to install Gitea Code Hosting Service on Ubuntu Linux. Gitea is a community-managed lightweight code hosting solution written in Go and published under the MIT license. It’s a painless self-hosted Git service similar to GitHub, Bitbucket, and GitLab.
How to Install Gitea Code Hosting Service on Ubuntu Linux
- Update Ubuntu system packages.
sudo apt update- Next, install dependencies for Gitea Code Hosting Service.
sudo apt install git wget mariadb-server- After the installation, secure the MySQL database.
sudo mysql_secure_installationSample output
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
haven't set the root password yet, you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password or using the unix_socket ensures that nobody
can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorisation.
You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'.
Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n] n
... skipping.
You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'.
Change the root password? [Y/n] n
... skipping.
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y
... Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!
Create Gitea database user
- Login to the MySQL database console using the command below.
sudo mysql -u root -p- Create database.
CREATE DATABASE gitea;- Then create a database user with your preferred password.
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON gitea.* TO 'gitea'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY "YourStrongPassword";- Next, flush all privileges.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES; - Exit the MySQL console using the following command.
exitInstall Gitea Code Hosting Service on Ubuntu Linux
- Get Gitea latest release from the download page and then download it using the
wgetcommand as shown below.
sudo wget -O /usr/local/bin/gitea https://dl.gitea.io/gitea/1.17.3/gitea-1.17.3-linux-amd64- Next, change the downloaded file permission using the following command.
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitea- Check the Gitea version using the command below.
gitea --version- After Gitea installation, create a user using the command below.
sudo adduser --system --shell /bin/bash --gecos 'Git Version Control' --group --disabled-password --home /home/git git- Run the following command to create Gitea directories.
sudo mkdir -pv /var/lib/gitea/{custom,data,log}- Change directories ownership using the command below.
sudo chown -Rv git:git /var/lib/gitea- Then modify the permissions of the main directory.
sudo chmod -Rv 750 /var/lib/gitea- Next, create a configuration directory.
sudo mkdir -v /etc/gitea- Change the created directory ownership using the command below.
sudo chown -Rv root:git /etc/gitea- Then change permissions.
sudo chmod -Rv 770 /etc/giteaCreate Systemd service file for Gitea
- Create a Systemd service file by running the command below.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/gitea.servicePaste the content below to the created file then save and close it.
[Unit] Description=Gitea After=syslog.target After=network.target [Service] RestartSec=3s Type=simple User=git Group=git WorkingDirectory=/var/lib/gitea/ ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/gitea web --config /etc/gitea/app.ini Restart=always Environment=USER=git HOME=/home/git GITEA_WORK_DIR=/var/lib/gitea [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
- Next, start Gitea and enable it to start on boot using the following command.
sudo systemctl enable --now giteaAccess Gitea Web Interface
- Gitea runs on port 3000 by default, open your web browser and enter your server IP or domain name followed by port 3000 e.g.
http://127.0.0.1:3000
- Enter your database name and password created for Gitea.
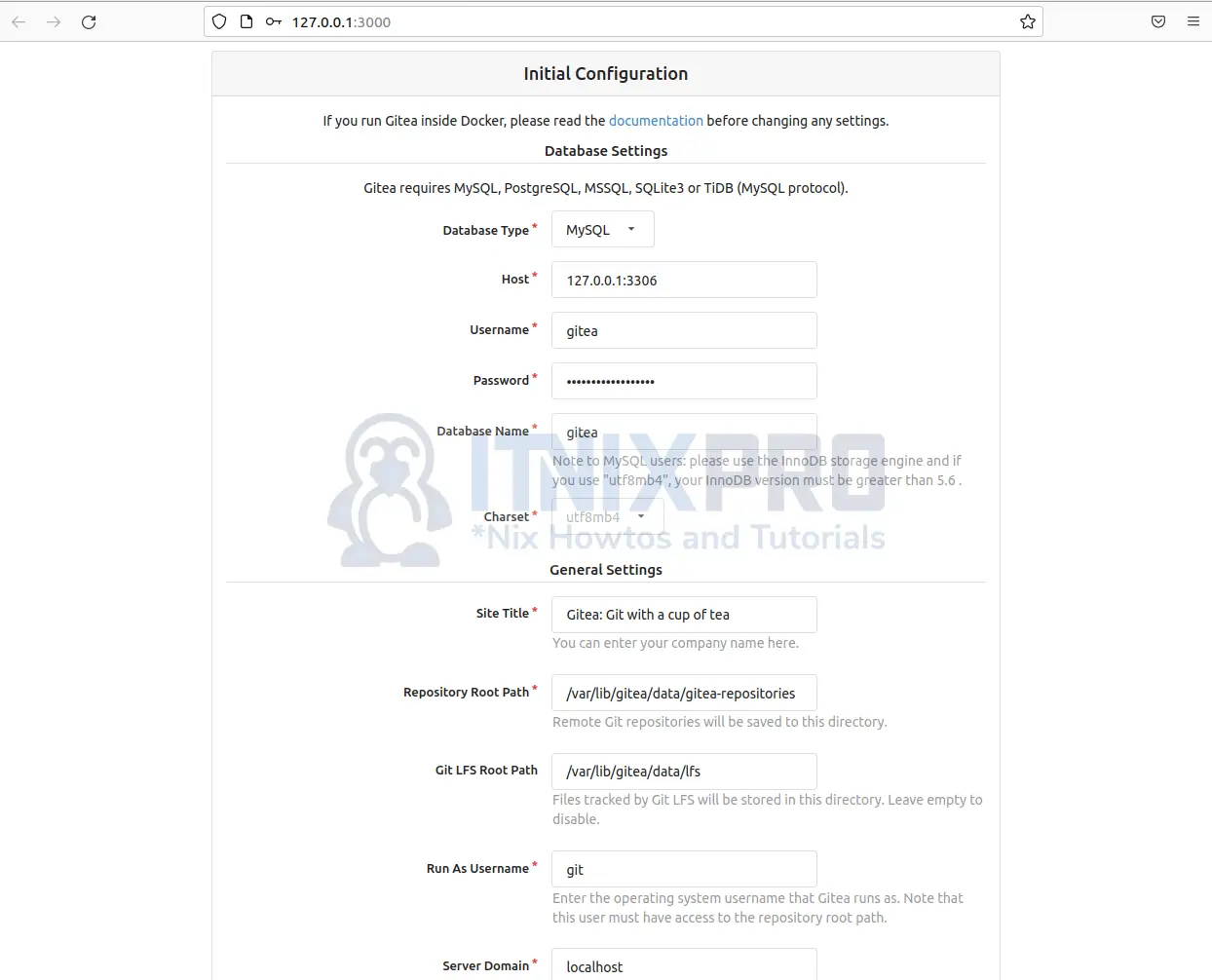
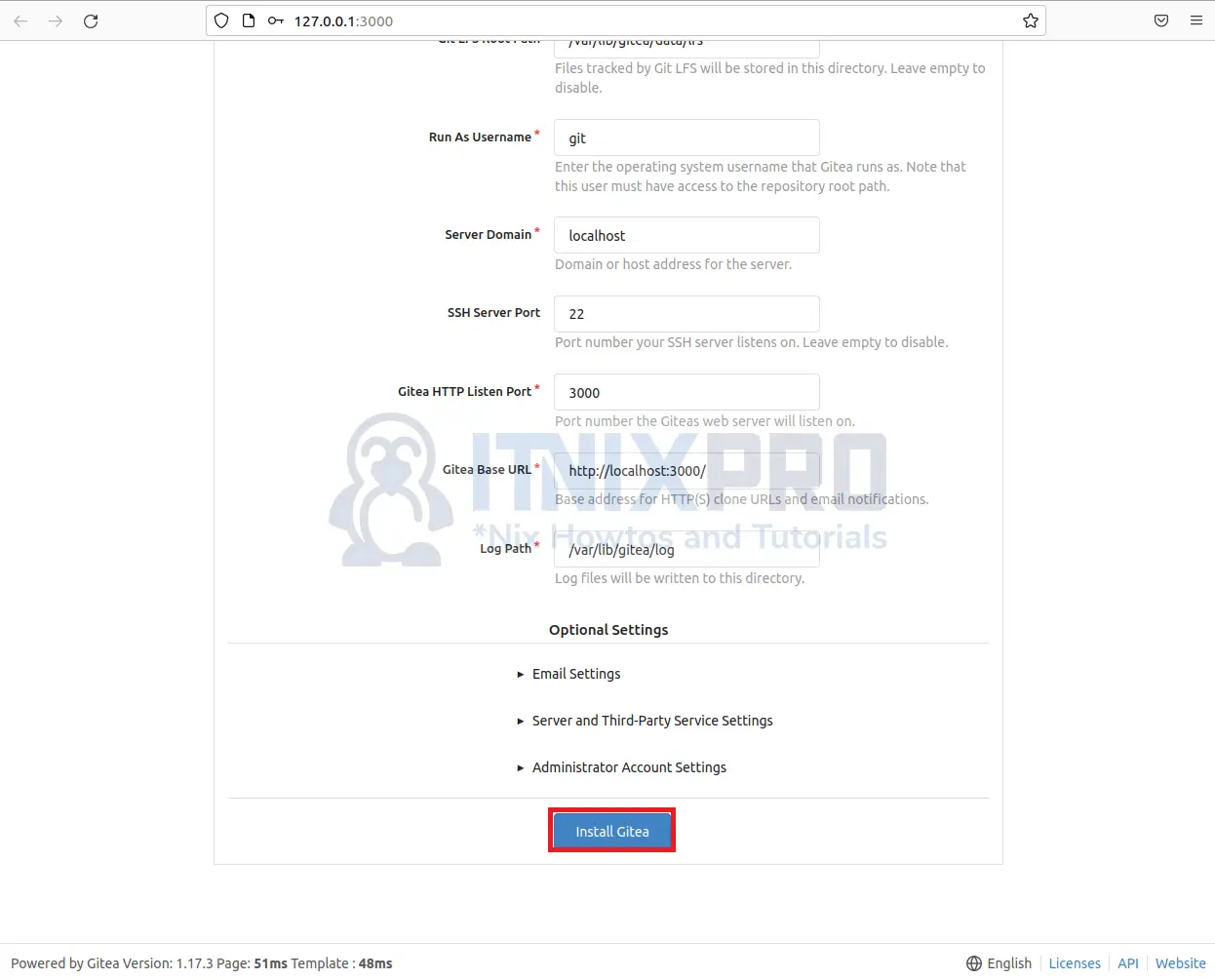
- Then scroll down and click on the Install Gitea button to complete the installation.
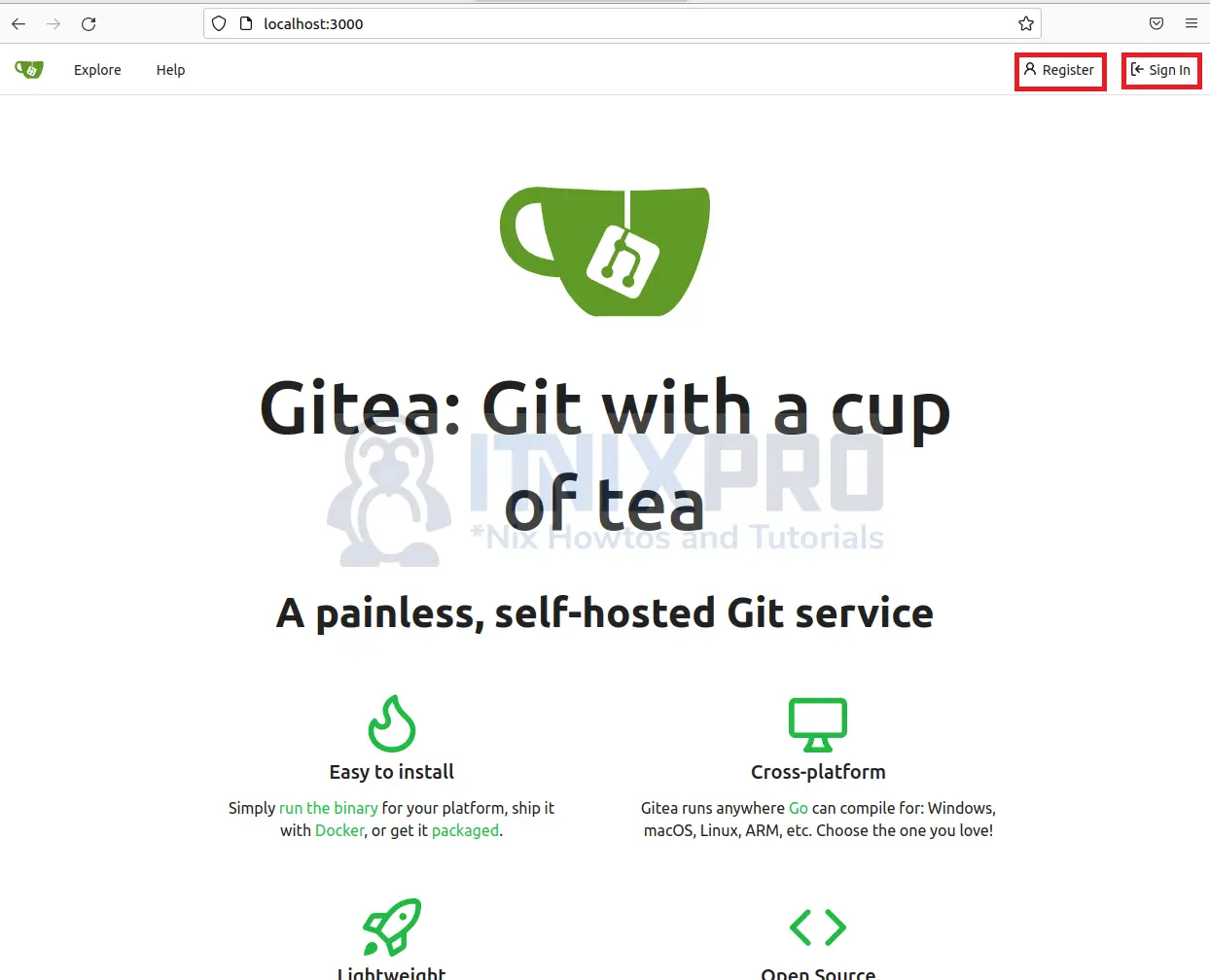
- You will be redirected to the home page where you can sign in or register an account.
- You have made it to the end of our article, we have gone through how to install Gitea Code Hosting Service on Ubuntu Linux.
Read more on Gitea Documentation
Other Tutorials
Create Data Map Visualization in Kibana
