You will uncover how to install CockroachDB cluster on Debian 11 in this article. CockroachDB is a cloud-based, globally distributed SQL database. There are three types of deployment options: dedicated, serverless, and self-hosted.
The main features of CockroachDB are scalability, fault tolerance, and availability of data. Data is geographically replicated across multiple servers, making it quicker and easier to access.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install CockroachDB cluster on Debian 11 using self-hosted deployment option with two servers.
Install CockroachDB cluster on Debian 11
Prerequisites
- Two or more Debian 11 servers
- Root privileges on both servers
The IP addresses for the servers/nodes are:
- Server 1 IP:
192.168.0.13 - Server 2 IP:
192.168.0.14
Connection through firewall
Allow connection through ports 8080 and 26257 on both your servers if your have firewall installed running.
- In the case of UFW firewall, use the commands:
ufw allow 8080/tcpufw allow 26257/tcpReload the firewall.
ufw reloadInstall CockroachDB cluster on Debian 11
If you are using CockroachDB in production environment, setup NTP server and use non-root user with superuser privileges.
Download the latest binary file on server 1 using wget commands. Unzip and copy the files to your system’s path
curl https://binaries.cockroachdb.com/cockroach-v22.1.0.linux-amd64.tgz | \
tar -xz && sudo cp -i cockroach-v22.1.0.linux-amd64/cockroach /usr/local/bin/Create a directory to store GEOS library files that provide spatial features.
mkdir -p /usr/local/lib/cockroachCopy the library files to the directory above:
sudo cp -i cockroach-v22.1.0.linux-amd64/lib/libgeos.so /usr/local/lib/cockroach/cp -i cockroach-v22.1.0.linux-amd64/lib/libgeos_c.so /usr/local/lib/cockroach/CockroachDB has now been installed on the first server. Confirm installation by checking the version:
$ cockroach version Build Tag: v22.1.2 Build Time: 2022/06/22 15:54:12 Distribution: CCL Platform: linux amd64 (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu) Go Version: go1.17.11 C Compiler: gcc 6.5.0 Build Commit ID: fc456a26830067b6dfbb8cd87e093a28d9b833d1 Build Type: release
Go to the second server and repeat the process.
Create clusters
To start with, create the first cluster on the first server by entering the --store, --listen-addr and --http-addr.
cockroach start --insecure --store=server1 --listen-addr=192.168.0.13:26257 \
--http-addr=192.168.0.13:8080 --join=192.168.0.13:26257,192.168.0.14:26258 \
--backgroundThis is what some of the flags mean:
- –store is the cluster for storing the data
- –listen-addr is the IP address for running on the server using port
25267. - –http-addr is the IP address the Cockroachdb web-based administration will be accessed via port
8080. - –insecure is for using unsecure(http) connection
Create the second cluster on the second server with the IP address(192.168.0.14)
cockroach start --insecure --store=server2 --listen-addr=192.168.0.14:26258 \
--http-addr=192.168.0.14:8081 --join=192.168.0.13:26257,192.168.0.14:26258 \
--backgroundFinally, join the clusters into one cluster to the first server.
cockroach init --insecure --host=192.168.0.13:26257Cluster successfully initializedAccess the web interface
Visit your browser and input the URL http://SERVER:8080 (SERVER is the IP address of server1), for instance, http://192.168.0.13:8080
The web-base management console opens as below.
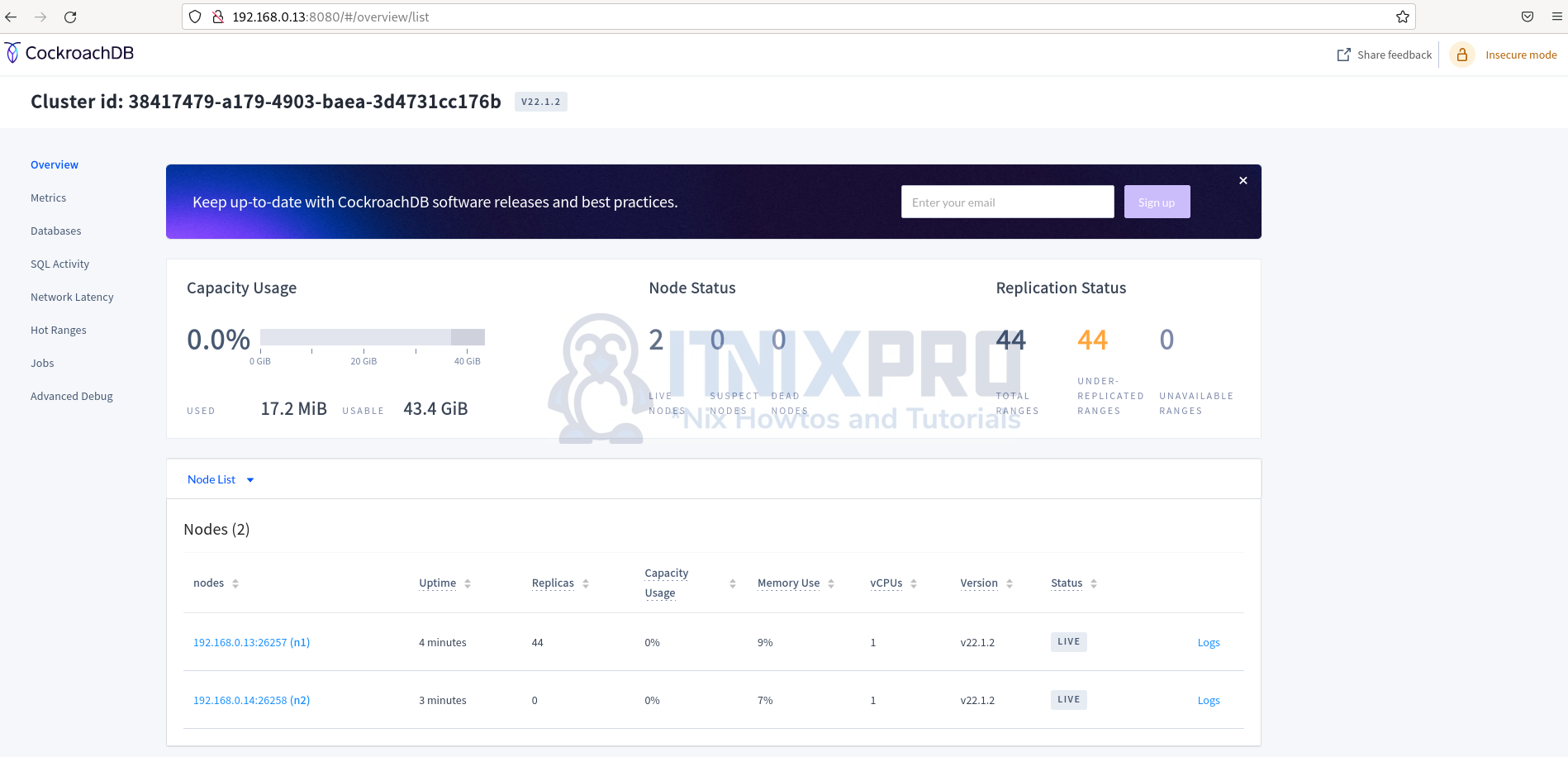
Testing the clusters
Write simple SQL statements to insert and check if data can be duplicated to all the servers.
Connect to server 1 cluster SQL console using the command:
cockroach sql --insecure --host=192.168.0.13:26257Create a database called itnixpro
CREATE DATABASE itnixpro;Next create a table users in this database
CREATE TABLE itnixpro.users (id INT PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT); Now insert some data to the table:
INSERT INTO itnixpro.users (id, name) values (1,'Barasa');Populate the data input:
select * from itnixpro.users; id | name -----+-------- 1 | Barasa (1 row) Time: 3ms total (execution 2ms / network 1ms)
Check if the data is duplicated to the second server. Connect to the second cluster on the second server.
cockroach sql --insecure --host=192.168.0.14:26257Display the data on the second cluster. The data has been duplicated to the second cluster.
select * from itnixpro.users; id | name -----+-------- 1 | Barasa (1 row) Time: 101ms total (execution 101ms / network 0ms)
Conclusion
This is the end of this article on how to install CockroachDB cluster on Debian 11.
More information is available on CockroachDB documentation
Similar interesting tutorials
Install CockroachDB on Ubuntu 22.04
