In our today’s tutorial, we will learn how to Install and Use Docker on Debian 12. You can create, run, and manage containers using the open-source container runtime engine known as Docker. The development and management of programs have been revolutionized by containerization, which has become an innovative technology in the IT sector thanks to Docker. It includes combining an application and its libraries into a small, portable object known as a container.
Docker Engine functions as a client-server program with:
- A computer hosting the dockerd daemon process.
- APIs that define interfaces that software can utilize to communicate with and give commands to the Docker daemon.
- A Docker client with a command line interface (CLI).
Table of Contents
Install and Use Docker on Debian 12
The following steps will guide you on how to install Docker on Debian 12 successfully.
Update Debian 12
Run the following command to update and upgrade the Debian 12 system, as it is recommended before we commence our installation;
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeReboot the system after the upgrade;
sudo reboot nowInstall the required packages
We will install prerequisites before we proceed with our Docker installation;
sudo apt install ca-certificates curl software-properties-common apt-transport-https gnupg lsb-release -yImport Docker’s GPG Repo Key
Set the correct permission of the /etc/apt/keyrings directory;
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
To import the GPG keys for the Docker repository, use the command below;
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
Now set the permission of docker.gpg file;
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
Add the Docker’s Repo to Debian 12
The Docker stable repository should now be added by running the command below;
echo \
"deb [arch="$(dpkg --print-architecture)" signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian \
"$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME")" stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/nullUpdate the system after adding the repo;
sudo apt-get updateInstall Docker on Debian 12
Now run the following command to install Docker on Debian 12 system;
sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-pluginAccept the installation prompt;
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: docker-buildx-plugin docker-ce-rootless-extras git git-man iptables liberror-perl libip6tc2 libslirp0 pigz slirp4netns Suggested packages: aufs-tools cgroupfs-mount | cgroup-lite git-daemon-run | git-daemon-sysvinit git-doc git-email git-gui gitk gitweb git-cvs git-mediawiki git-svn firewalld The following NEW packages will be installed: containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-ce docker-ce-cli docker-ce-rootless-extras docker-compose-plugin git git-man iptables liberror-perl libip6tc2 libslirp0 pigz slirp4netns 0 upgraded, 14 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Need to get 123 MB of archives. After this operation, 459 MB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y
Start and Enable Docker on Debian 12
After successful installation of Docker on Debian 12, run the following commands to start and enable it to run on boot;
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable dockerCheck the status of the Docker service;
systemctl status dockerOutput;
● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2023-09-21 05:12:35 EAT; 2min 52s ago
TriggeredBy: ● docker.socket
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
Main PID: 15535 (dockerd)
Tasks: 9
Memory: 29.5M
CPU: 521ms
CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service
└─15535 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
Sep 21 05:12:32 itnixpro systemd[1]: Starting docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine...
Sep 21 05:12:32 itnixpro dockerd[15535]: time="2023-09-21T05:12:32.137933935+03:00" level=info msg="Starting up"
Sep 21 05:12:32 itnixpro dockerd[15535]: time="2023-09-21T05:12:32.983365426+03:00" level=info msg="Loading containers:>
Sep 21 05:12:34 itnixpro dockerd[15535]: time="2023-09-21T05:12:34.073875192+03:00" level=info msg="Loading containers:>
Sep 21 05:12:35 itnixpro dockerd[15535]: time="2023-09-21T05:12:35.711087696+03:00" level=info msg="Docker daemon" comm>
Sep 21 05:12:35 itnixpro dockerd[15535]: time="2023-09-21T05:12:35.711999093+03:00" level=info msg="Daemon has complete>
Sep 21 05:12:35 itnixpro dockerd[15535]: time="2023-09-21T05:12:35.814593977+03:00" level=info msg="API listen on /run/>
Sep 21 05:12:35 itnixpro systemd[1]: Started docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine.
Confirm the installed version of Docker;
docker versionOutput;
Client: Docker Engine - Community Version: 24.0.6 API version: 1.43 Go version: go1.20.7 Git commit: ed223bc Built: Mon Sep 4 12:32:10 2023 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 Context: default Server: Docker Engine - Community Engine: Version: 24.0.6 API version: 1.43 (minimum version 1.12) Go version: go1.20.7 Git commit: 1a79695 Built: Mon Sep 4 12:32:10 2023 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 Experimental: false containerd: Version: 1.6.24 GitCommit: 61f9fd88f79f081d64d6fa3bb1a0dc71ec870523 runc: Version: 1.1.9 GitCommit: v1.1.9-0-gccaecfc docker-init: Version: 0.19.0 GitCommit: de40ad0
In order to run Docker commands without using the sudo command, add your user to the Docker group;
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
newgrp dockerDocker Example Usages on Debian 12
in this section, we will show you how to deploy an application with Docker.
Deploy Nginx Application Using Docker
To run the Nginx application in Docker, execute the following command to deploy it;
sudo docker run --name nginx-app -p 80:80 -d nginx:latestOutput;
Unable to find image 'nginx:latest' locally latest: Pulling from library/nginx a803e7c4b030: Pull complete 8b625c47d697: Pull complete 4d3239651a63: Pull complete 0f816efa513d: Pull complete 01d159b8db2f: Pull complete 5fb9a81470f3: Pull complete 9b1e1e7164db: Pull complete Digest: sha256:32da30332506740a2f7c34d5dc70467b7f14ec67d912703568daff790ab3f755 Status: Downloaded newer image for nginx:latest 82533f5191a92ef134bcfabc7e2d097a5f946671e22a87dd46b27f1062c60951
Verify that nginx-app container is created;
docker psOutput;
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
82533f5191a9 nginx:latest "/docker-entrypoint.…" About a minute ago Up About a minute 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, :::80->80/tcp nginx-appAs per the output above, Nginx application is up and running.
Access Deployed Application(Nginx)
Navigate to your browser and type http://<your-ip-address> to access the Nginx application. Remember to replace “your-ip-address” with your actual IP. In my case, it will be http://192.168.56.101;
You will land on the following Nginx page;
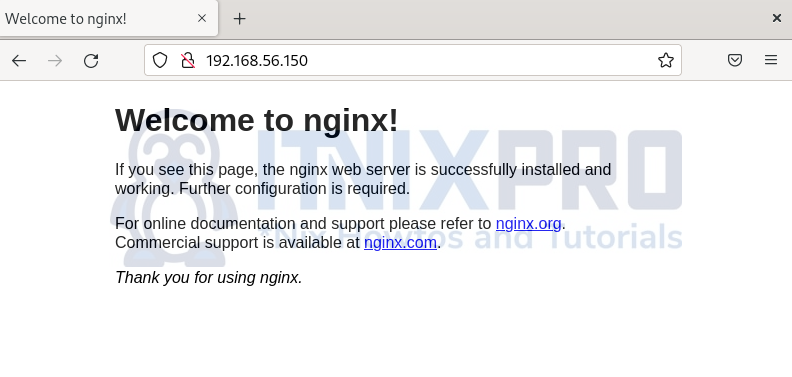
From the above output, Nginx is now running.
The End!
We have come to an end with our tutorial on how to Install and Use Docker on Debian 12. In the process, you learn how to deploy applications using Docker. We deployed Nginx as our example. Enjoy running your application using Docker.
Related Guides
Setup Docker Swarm Cluster on Ubuntu 22.04
